Agilent Technologies B1500A Service Manual Page 57
- Page / 110
- Table of contents
- BOOKMARKS
Rated. / 5. Based on customer reviews


Module 5
Basic Measurement
5-37
I
B
Re = 735 m
Ω
Rcable = 214 m
Ω
V
C
monitor
Slope = 1/Re
(Kelvin)
Slope = 1/(Re+Rcable)
(Non-Kelvin)
Ib (mA)
Vc (mV)
0
50
20
0.1
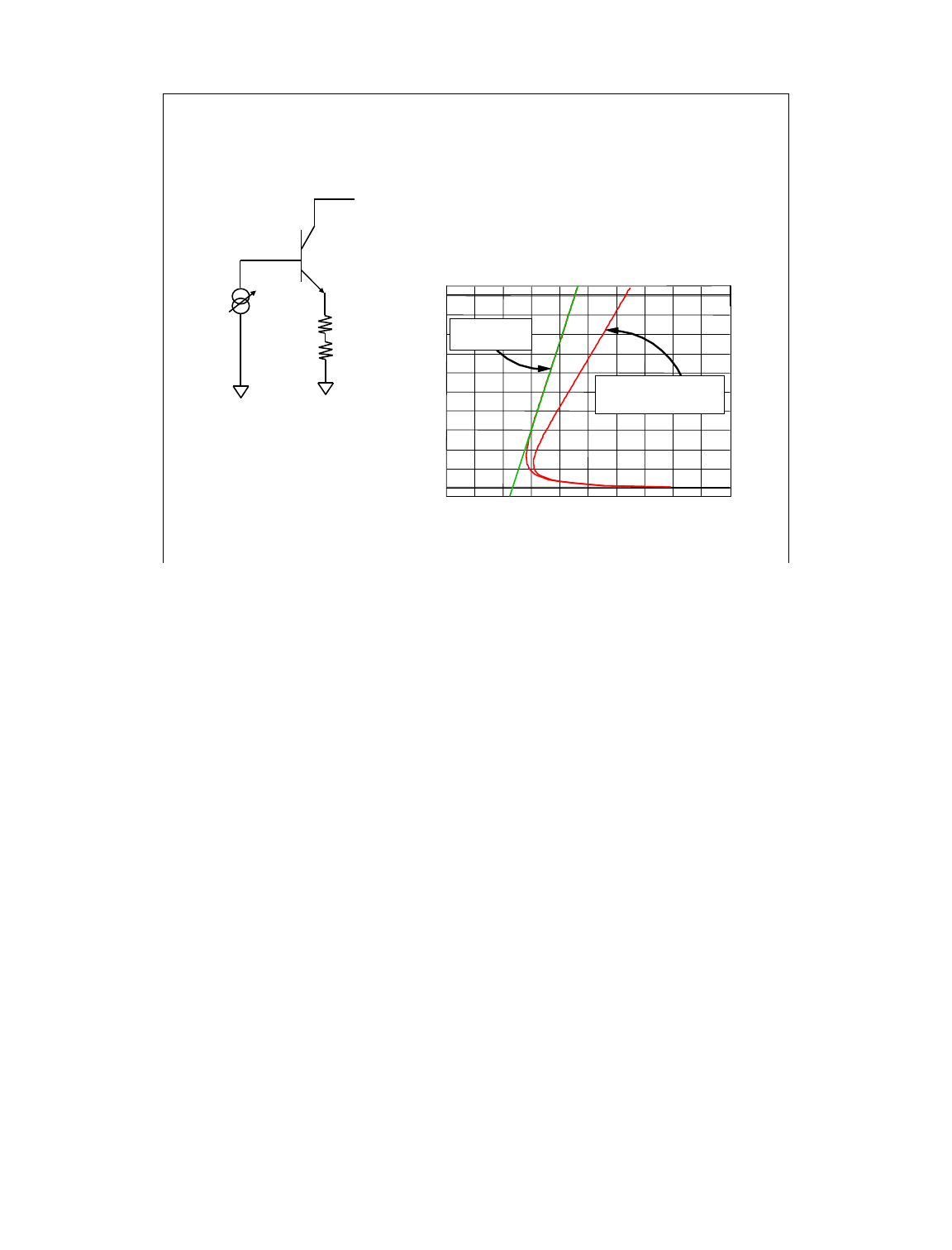
Why Kelvin Measurements?
In the example above, the device is connected with a SMU on the base sweeping current, a voltmeter
on the collector, and the emitter is grounded with a Kelvin SMU. The base SMU does not have to be
Kelvin since we are only forcing current and do not care about measuring the cable loss in the base.
Also, the collector SMU is being used only as a high impedance voltmeter, so there is no cable loss
in this lead.
The emitter on the other hand, must be connected to a Kelvin SMU. Because of this, we can
compensate for the 0.214 ohm path through the cable and fixture. From the graph we can see the
emitter resistance is 0.735 ohm when compensated using the Kelvin connection. Non-Kelvin
resistance is 0.949 ohm, due to the extra 0.214 ohm cable and fixture resistance error.
- Agilent B1500A 1
- Semiconductor Device 1
- Analyzer 1
- Manual Part Number 2
- Warranty 2
- Technology Licenses 2
- Restricted Rights Legend 2
- In This Manual 4
- Class Exercises 6
- .xtr files 7
- Demo.xpg file 7
- .xtd files 7
- 1 ohm Resistor 10
- 1.1 kohm Resistor 10
- 511 kohm Resistor 10
- 0.1 uF Capacitor 10
- Module 1. Introduction 13
- Module 2. Getting Started 13
- Module 5. Basic Measurement 15
- Contents 20
- Contents-8 20
- 5 Basic Measurement 21
- In This Module 22
- SMU Block Diagram 23
- Basic Sweep Measurement 24
- Sweep Measurement Modes 25
- Combining VAR1, VAR1’, VAR2 25
- Why Four SMUs? 26
- Class Exercise 27
- SMU Triax Connection 28
- Wrong Triaxial Hookup 29
- Jumper Leads – MOS transistor 30
- To Import Demo Data 31
- To Get Setup Data 32
- Classic Test – Channel Setup 33
- Do not abort on 34
- Classic Test – Display Setup 35
- To Start Measurement 36
- Data Display Window – Graph 37
- Data Display Window - List 38
- Paste to Notepad 39
- To Copy List Data 39
- Application Test 40
- Module 5 41
- Basic Measurement 41
- SMUs May Be Connected 42
- 200 V Resistor Sweep 43
- 200 V BVceo 43
- Two SMUs in Series 44
- Voltage across resistor 44
- VR = V1-V2 44
- VAR1' Ratio = -1 45
- Measurement and Display Pages 45
- Graphics Page 0 to 200 V 46
- 200 mA Output 47
- Two SMUs in Parallel 48
- Current in resistor 48
- Itotal = I1+I2 48
- VAR1' Ratio = 1 49
- Resistor 50
- Graphics Page 0 to 200 mA 50
- Cabling and Fixturing Issues 51
- Simplified Diagram 52
- Kelvin Triaxial Cable 56
- Why Kelvin Measurements? 57
- Cable Connections 59
- Class Example - Jumper Leads 60
- 2. Click Recall button 61
- To Get REKELV Test Setup: 61
- Single Kelvin Measurement 62
- Non-Kelvin Measurement 63
- To Kelvin Probe 64
- To Guarded Chuck 64
- Connector Plate 65
- Guarded to within 2mm of tip 67
- Single Triax Kelvin Triax 67
- Triaxial Probes 67
- Simplifying RF Connections 68
- Interlock Connection 69
- 16493J-001 1.5 m cable 70
- 16493J-002 3.0 m cable 70
- 16442A/B Fixture 70
- 16058A Fixture Compatibility 71
- 6 Low Current Measurement 73
- Low Current Measurement 75
- What is possible? 75
- Challenges 76
- Clean Probing Environment 77
- What is Required? 77
- Where to Start? 78
- Low Current 79
- Calibration & Zero Cancel 79
- Calibration 80
- Measurements Near Zero fA 81
- ZERO CHECK - No cable 82
- Using Default SMU Setup 82
- Delete SMU1 and SMU2 83
- Change Mode to V and 83
- Function to VAR1 83
- ZERO CHECK 83
- Channel Setup 83
- Do not change this screen 84
- Display Setup 86
- Bumping cable 88
- Bending Cable 88
- Effect of cable movement 88
- Appendix: Using ASU 89
- Configuration 90
- HRSMU+ASU 91
- Low Current Subthreshold 92
- SD214DE MOS Subthreshold 94
- Trade Off Speed vs Accuracy 95
- What is measured? 96
- Low Current Gummel Plot 97
- Module 6 98
- Small step size 99
- Negative sweep values 99
- Range and Integration Time 100
- Maximum resolution 100
- Gummel Plot 100
- LOW CURRENT MEASUREMENT 101
- Gummel Plot With 102
- ULTRA LOW CURRENT 103
- Subthreshold Curve 103
- Small STEP: 100 mV 104
- Large HOLD TIME: 3 sec 104
- Measurement Setup 104
- Set long integration time 106
- Leakage to fA levels 107
- Chuck must be guarded 107
- Fowler-Nordheim (FN) Plot 108
- Negative sweep 109
- Accumulation mode 109
- Wait for 5 V initial step 109
- FOWLER-NORDHEIM PLOT 109
- Measurement Page 109
- Low Current Gate Oxide Meas 110
- Using Guarded Chuck 110
 (628 pages)
(628 pages)







Comments to this Manuals